Are you dreaming of owning a home in the United States of America (USA or the U.S.)? Many people worldwide are drawn to the idea of having a house in the United States, whether for vacation, investment, or a fresh start. The good news is that buying property as a foreigner is possible. But before you jump in, there are some critical things you need to understand.
So, what exactly do you need before starting your homeownership journey in the U.S.? Read on to find out!
1. Property Ownership Comes With Tax Obligations
Buying real estate in the United States comes with financial responsibilities, and taxes are a major part of that picture. These vary depending on property location and local rates. In some cities and counties, they can represent a significant ongoing expense, so it's crucial to plan accordingly.
Foreign nationals who own property in the U.S. must also consider the broader tax implications. If the home generates rental income, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires you to report it and pay income taxes. In some instances, capital gains tax may apply when the property is sold.
Navigating U.S. taxes for non-residents can be complex, especially for international buyers unfamiliar with these rules. Consulting a professional who understands foreign investment and tax obligations can help you manage these responsibilities and avoid unexpected costs.
2. You'll Need a Real Estate Agent Familiar With Foreign Buyers
Choosing a real estate agent who regularly works with foreign nationals can make the process smoother. While many agents know the local market, not all are familiar with the specific needs of non-resident buyers navigating U.S. property laws.
An experienced professional can explain legal regulations, property location requirements, and state-specific rules. They'll also help you avoid issues that international buyers often face during the transaction.
Explore Utah Real Estate

83 W 850 S, Centerville, UT
$815,000
Bedrooms: 5 Bathrooms: 3 Square feet: 3,999 sqft
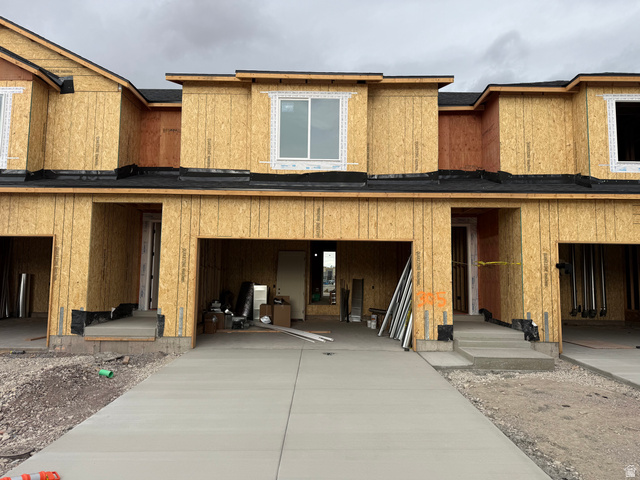

653 E RYEGRASS DR #305, Eagle Mountain, UT
$387,900
Bedrooms: 3 Bathrooms: 3 Square feet: 1,985 sqft
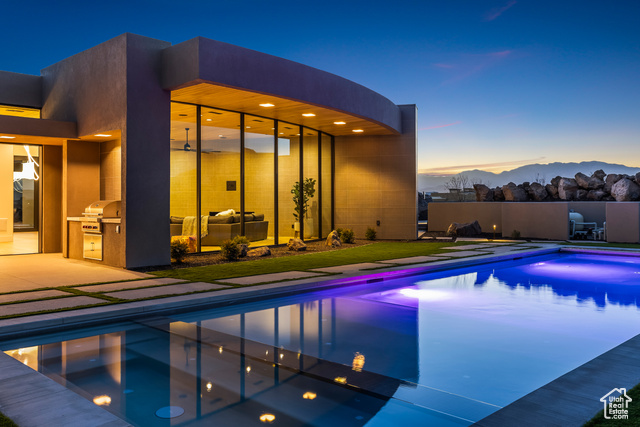

2031 N LAVA ROCK CIR #107, St George, UT
$4,185,000
Bedrooms: 4 Bathrooms: 5 Square feet: 5,404 sqft
This kind of guidance becomes even more vital if you're unfamiliar with the U.S. real estate market. A skilled agent can explain every step clearly and connect you with financial institutions and legal experts who handle transactions involving foreign investors. This will help reduce confusion and give you more confidence as you move forward.
3. A U.S. Bank Account and ITIN Are a Requirement
You'll need a U.S. bank account to complete any real estate transactions in the country. Most property purchases require funds to move through local financial institutions, especially when dealing with mortgage loan disbursements or escrow arrangements. International buyers should plan ahead, as opening a U.S. bank account can take time, particularly if you're still overseas.
Along with the account, you'll need an individual taxpayer identification number (ITIN) if you don't qualify for a Social Security number (SSN). This number is essential for paying property taxes and reporting rental income from your investment property. It also helps streamline your loan application and simplifies communication with lenders.
4. Financing Might Be a Challenge
Financing real estate in the U.S. can be more complicated for foreign nationals than for citizens. Many mortgage lenders are cautious when dealing with applicants who lack a U.S. credit report or established financial history within the country. Without a strong credit score or verifiable income in U.S. dollars, you may face more demanding requirements during the loan application process.
Because of this, foreign investors often need to provide a larger down payment to secure approval. In many cases, mortgage requirements can include 30 percent or more upfront. Interest rates may also be higher because lenders view these loans as carrying greater risk.
Some international buyers choose to make an all-cash transaction instead, which avoids delays and simplifies approval. If you plan to seek financing, compare options and consider working with a U.S. mortgage lender familiar with international credit history and foreign income documentation.
More Properties You Might Like

2098 E GOOSE RANCH RD, Vernal, UT
$103,000
Square feet: 274,864 sqft

2148 E GOOSE RANCH RD, Vernal, UT
$116,000
Square feet: 309,276 sqft
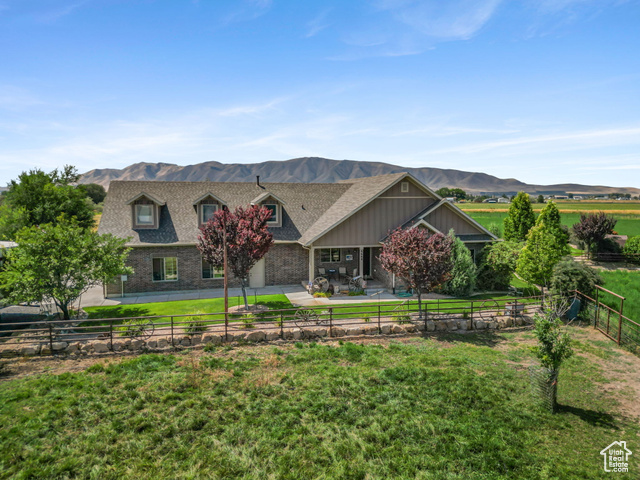

6668 S 3200 W, Spanish Fork, UT
$2,074,000
Bedrooms: 3 Bathrooms: 3 Square feet: 2,560 sqft
5. Understand the Closing Process
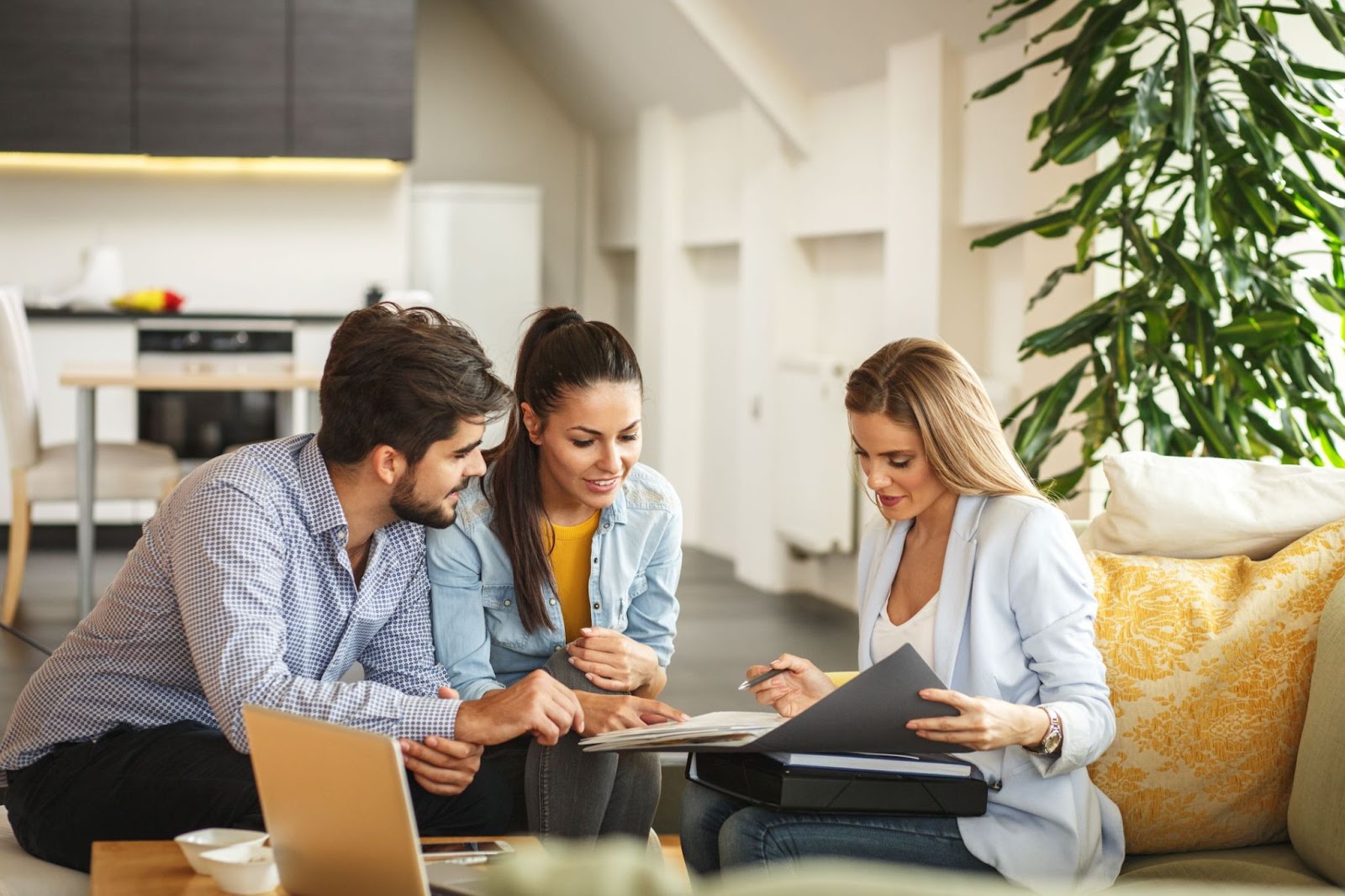

Closing on real estate in the U.S. involves several essential steps. You'll need to sign legal documents, pay the remaining costs, and complete the transfer of ownership. For foreign nationals, this part of the process may happen remotely or through a legal representative. In many cases, buyers choose to grant power of attorney to someone in the U.S. who can handle the paperwork and attend the closing on their behalf.
The final costs often include a title search, home insurance, legal fees, and inspection charges. These expenses usually range from two to five percent of the total property value.
Be sure to review every document carefully during this process to ensure the title report is accurate. You might also need to show where your funds originated to prevent money laundering. Prepare in advance to complete the transaction smoothly and avoid delays.
6. Know the Long-Term Ownership Responsibilities
Once you've purchased real estate in the United States, the work doesn't stop there. You'll need to maintain the property, cover regular expenses, and follow local rules, especially if your home is part of a housing cooperative or subject to a homeowners' association. If you're not living in the home year-round, it may be worth hiring a property manager to oversee maintenance and handle tenant concerns if the property is used as a rental.
It's also crucial to stay aware of changes in property value, tax obligations, and state regulations that may affect your investment. Laws surrounding foreign nationals and property ownership can evolve, and staying informed helps protect your long-term interests.
Conclusion
Buying a home in the U.S. as a foreign national is possible, but it comes with unique steps and responsibilities. From financing and taxes to legal paperwork and long-term upkeep, understanding the whole process can help you make smarter decisions. With the right support and preparation, owning a U.S. property can be a smooth and rewarding experience.